Why SMS Based MFA Is Falling Short Of Security Expectations
What Is SMS-Based MFA?
As technology changes and security threats become more sophisticated, the ability to keep accounts and information secure is more important than ever. SMS-based Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) has long been touted as the gold standard for account security. However, with many of its inherent vulnerabilities, can it really provide the level of security needed? In this article, we'll discuss the risks of SMS-based MFA and explore more secure alternatives including Multi-Factor Authentication Tokens, Biometric Authentication, and Push Notifications.
What Are the Risks of SMS-Based MFA?
Modern security systems are in place to protect our personal data and identities on the internet. For example, Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and Two-Factor authentication (2FA) are widely used to protect online accounts. One type of MFA or 2FA that is often used is SMS-based authentication. This involves the user receiving a text message with a security code to then enter into a website or app in order to prove their identity. While SMS-based MFA is a convenient and widely used security method, it does come with a few risks and drawbacks.
The first risk of SMS-based MFA is that SMS messages are not encrypted. This leaves the security code vulnerable to interception and malicious use by hackers who can then use the code to access the user’s account. While this risk can be minimized with the use of other types of MFA, such as biometric authentication, it is still a valid concern.
Another risk of SMS-based MFA is that the user’s mobile phone number can be spoofed or stolen. This means that a malicious third party can send an SMS message with a security code as if it were coming from the user’s legitimate phone number. When this happens, the code could be used to access the user’s account without them knowing.
Lastly, SMS-based MFA can be unreliable due to the instability of mobile networks. This can mean that the security code isn’t sent or is sent much later than it should have been, making it difficult to authenticate.
In conclusion, while SMS-based MFA is a convenient and widely used security method, it does come with a few risks and drawbacks. Therefore, it’s important to weigh these risks against the benefits before deciding to use it for your own security needs.
Poor Mobile Network Connectivity
Poor mobile network connectivity can be a major headache for businesses, particularly when it comes to security. Having a secure and reliable connection is critical for a wide range of services and processes, but mobile networks can often be unreliable or fail completely. To guard against security risks and ensure easy access to services, it is important for businesses to consider Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA). These technologies can be used in conjunction with Short Message Service (SMS) to provide an extra layer of security and ensure that only authenticated users have access to services. By using MFA and 2FA, businesses can improve their security and protect their data even if their mobile network connection is unstable.
Phone Number Porting Attacks
Phone number porting attacks are a growing concern in the world of cybersecurity. These attacks involve a malicious actor hijacking a victim's phone number by masquerading as the victim to a telecommunications provider. This allows the malicious actor to perform actions such as bypassing two-factor authentication (2FA), intercepting SMS messages, and even gaining access to the victim's online accounts. To protect against these kinds of attacks, organizations should adopt additional security measures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and monitoring of SMS messages. The use of these measures can help decrease the chances of falling victim to a phone number porting attack.
Social Engineering
Social Engineering is the use of deception techniques to gain access to confidential information, such as passwords and PIN numbers. While it has always been a concern within the security industry, social engineering has become increasingly common with the rise of mobile device technology and SMS messages. In particular, two-factor authentication (2FA) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) can be vulnerable to social engineering attacks. It is important to understand the risks posed by social engineering and take steps to protect yourself and your organization. Taking steps such as educating users on the risks of SMS messages, implementing strong authentication protocols, and using anti-phishing solutions can help reduce the risks associated with social engineering.
More Secure Alternatives to SMS-Based MFA
The traditional way of verifying user identity and access privileges is through SMS-Based Multifactor Authentication (MFA). However, this method of authentication has become increasingly vulnerable to a variety of attacks and is becoming less secure. While SMS-based MFA may still be used, it is important to understand the security implications and consider more secure alternatives.
With the advent of mobile and cloud authentication, more secure methods can be used to supplement or replace traditional SMS-based MFA. These alternatives are typically based on two-factor authentication (2FA) protocols, which are more secure and add an extra layer of security to the authentication process. 2FA is often provided by third-party identity providers, such as Authy, Google Authenticator, or Microsoft Authenticator, and is designed to ensure that login attempts are only successful if both an authorized user's password and an additional verification code are correctly entered.
Strong authentication protocols, such as OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect, eliminate the need for SMS-based authentication by enabling users to securely authenticate their identity without having to share their personal information or passwords. These protocols allow users to securely communicate with their identity provider and access applications without the need for SMS-based MFA.
Finally, biometric authentication (including Fingerprint, Facial, and Voice recognition), while still relatively new, is gaining traction as an increasingly secure way to verify user identity. This technology uses an individual's unique biometrics to verify identity, allowing users to access their accounts with more secure, unique, and convenient security measures.
Overall, although SMS-based MFA is still widely used, more secure alternatives are readily available and should be considered as an additional layer of security. By considering these more secure alternatives, users can be sure that their data is safe and secure from any potential threats.
Multi-Factor Authentication Tokens
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) tokens are an essential security measure for protecting online accounts and personal data. MFA tokens work by requiring the user to provide not only a password, but also an additional authentication factor that is typically sent to a registered mobile device. This type of authentication is often referred to as 2-Factor Authentication (2FA) or SMS-based authentication and requires users to enter both their password and a unique code sent to their registered device in order to access an account. By providing an additional layer of security, MFA tokens make it more difficult for malicious actors to gain access to a user account. As such, more and more organisations are encouraging their customers to use MFA tokens to protect their accounts.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication is a secure and efficient way to protect your personal data and digital assets. Unlike traditional security measures such as SMS-based or password-based authentication, biometric authentication uses unique physiological or behavioral characteristics of an individual to verify their identity. Popular methodologies of biometric authentication include fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and voice recognition. Moreover, multi-factor authentication (MFA) and two-factor authentication (2FA) protocols can be used in combination with biometric authentication to offer even greater security. By implementing biometric authentication, organizations can ensure that only authorized individuals have access to their sensitive data.
Push Notifications
Push notifications provide an effective and secure method for users to receive timely updates about their accounts and services. By sending push notifications directly to a user's device, companies can keep users in the loop without compromising security. Unlike SMS, push notifications can be used in conjunction with multi-factor authentication (MFA) and two-factor authentication (2FA). Additionally, companies can program their push notifications to be tailored to individual user preferences. Push notifications are a convenient and secure way of providing users with important updates in a timely manner.
Conclusion
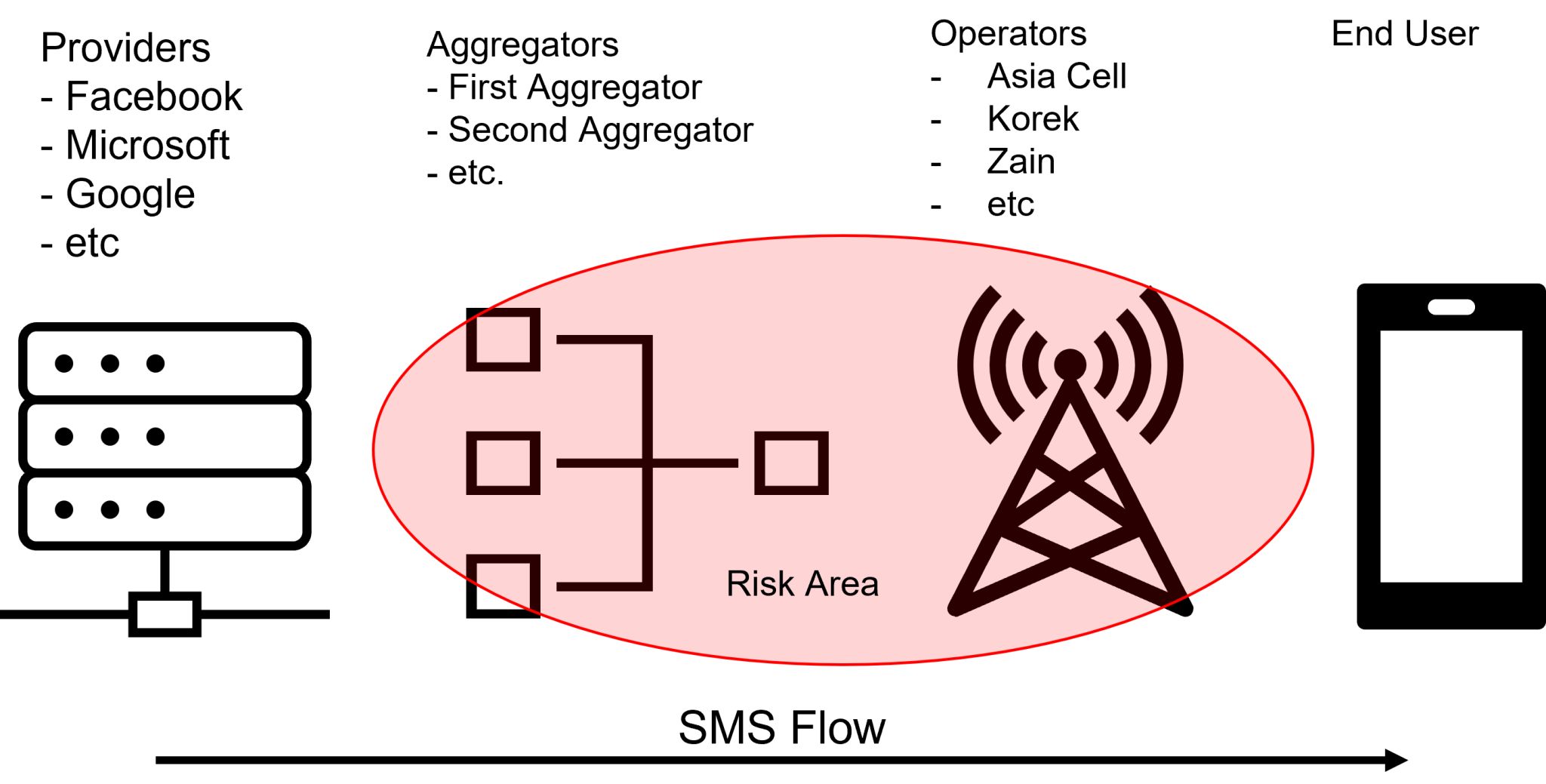
SMS can indeed be stolen or intercepted by third-party aggregators, resellers, or other service providers who have access to the SMS traffic. This is especially true in cases where SMS traffic is routed through multiple parties or when a user employs a third-party SMS provider or API to send messages. In such cases, it's essential to ensure that the SMS provider or aggregator you choose has appropriate security measures in place to protect your messages and sensitive information from unauthorized access or interception. It's also important to regularly monitor your SMS traffic and report any suspicious activity to your service provider or law enforcement.
Suggestions for Facebook, Microsoft, Google, etc:
- Password reset must be based on extra factors not only OTP by SMS.
- In case user changed sensitive account information, extra security verification must be applied in parallel with SMS OTP.